1) AGENTS
a) Lidocaine
i) General
(1) Local anesthetic with quick onset and short duration of action
(a) Onset = few seconds to a few minutes
(b) Duration = 1 to 2 hours
ii) Dose
(1) Dogs
(a) 1.0 to 5 mg/kg (0.5 to 2.5 mg/lb)
(2) Cats
(a) 1.0 to 2.5 mg/kg (0.5 to 1.0 mg/lb)
iii) Precautions
(1) Potential CNS toxicity
(a) Usually manifests as seizure activity
iv) Cost
(1) Low
b) Mepivacaine
i) General
(1) Local anesthetic with quick onset and moderate duration of action
(a) Onset = 5 to 10 minutes
(b) Duration = 2 to 3 hours
ii) Dose
(1) Dog
(a) 5 mg/kg (2.5 mg/lb) in dogs
(2) Cat
(a) 2.5 mg/kg (1.0 mg/lb)
iii) Precautions
(1) IV use is not currently recommended
iv) Cost
(1) Low
c) Bupivacaine
i) General
(1) Local anesthetic with slower onset and longer duration of action
(a) Onset = 20 to 30 minutes
(b) Duration = 3 to 5 hours
ii) Dose
(1) Dog and cat
(a) 1.0 to 2.0 mg/kg (0.5 to 1.0 mg/lb)
iii) Precautions
(1) Never give bupivacaine IV
(2) Potentially fatal cardiac toxicity
(a) Calculate doses carefully and aspirate carefully to guard against
intravascular administration
(3) There is some debate about the use of intrapleural bupivacaine if a pericardiectomy has been
performed due to the increased potential for cardiac toxicity
iv) Cost
(1) Moderate
2) APPLICATIONS
a) First, consider adding an opioid to the local anesthetic
i) Both 0.075 mg/kg (0.035 mg/lb) morphine and 0.003 mg/kg (0.0015
mg/lb) buprenorphine have been shown to effectively double the analgesic
duration when combined with lidocaine and bupivacainein humans 1,2
b) Outpatient/awake patient use
i) Mix 0.9 cc Lidocaine, 0.1 cc sodium bicarbonate, and 2 cc of
sterile water
(1) Reduced sting
(2) Volume is more important than concentration
(3) Increasing the bicarbonate percentage above 10% is not recommended
as it will lead to precipitation of the drug
| |
|
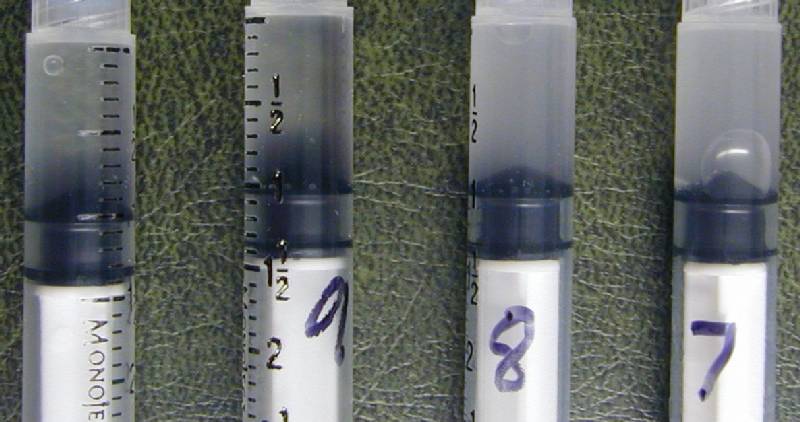
The syringe at left is 100% lidocaine. The second
from left (9) is 90% lidocaine 10% bicarbonate. The third syringe
from left (8) is 80% lidocaine 20% bicarbonate. The syringe to the
right (7) is 70% lidocaine 30% bicarbonate. Precipitate is clearly
seen in the 20% and 30% bicarbonate solution. |
c) Splash block
i) Drip on or in SubQ space at closure of skin wound
ii) The effectiveness of splash blocks is in question
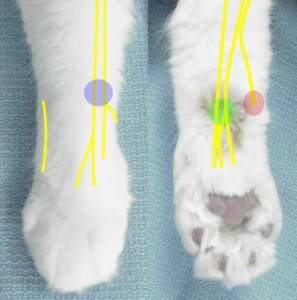
d) Ring blocks
i) Mix 1.0 mg/kg (0.5 mg/lb) bupivacaine with 1.0 mg/kg (0.5 mg/lb)
lidocaine and:
(1) Either 0.075 mg/kg (0.035 mg/lb) morphine or 0.003 mg/kg (0.0015
mg/lb) buprenorphine to effectively double the duration of analgesia 1,2
(2) Sterile water q.s., if needed, to total 1 cc volume for cats less
than 2.5 kg (5 lb).
(3) Sterile water q.s., if needed, to total 2 cc volume for cats 2.5 kg
(5 lb) and over.
ii) Inject subcutaneously at the three sites demonstrated below:
iii) You may drop the lidocaine if given prior to spay (gives
bupivacaine time to take effect)
iv) Bupivacaine has significant potential to cause cardiac toxicity
(1) Calculate dose carefully
v) DO NOT USE EPINEPHRINE
CONTAINING AGENTS
v) Click
here for an MS Excel Ring Block dose calculator
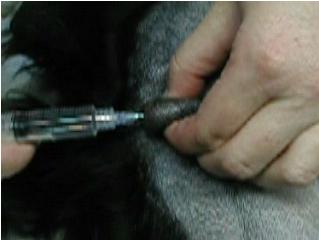
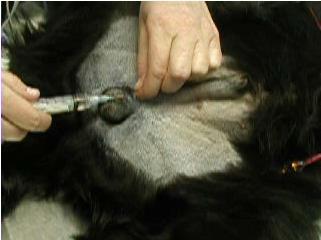
e) Intra-testicular blocks
i) This is a very effective, low-cost application of local anesthetic
agents
ii) Mix 1.0 mg/kg (0.5 mg/lb) bupivacaine with 1.0 mg/kg (0.5 mg/lb)
lidocaine and:
(1) Either 0.075 mg/kg (0.035 mg/lb) morphine or 0.003 mg/kg (0.0015
mg/lb) buprenorphine to effectively double the duration of analgesia1,2
iii) Use a 25g 5/8” needle for most cats and a 22g 1 to 1 ½“ needle
for dogs
iv) Place the needle through the testicle starting from the caudal pole
aiming for the spermatic cord
v) It is OK, even desirable, for the needle to exit the testicle
proximally as it is the spermatic cord that will receive the direct clamp
stimulation
vi) ASPIRATE BEFORE INJECTING
(1) Inject, expecting firm
backpressure, while withdrawing the needle
(2) Expect to use about 1/3 to ½ of the drug volume per testicle
leaving the organ firmly turgid
vii) Repeat for other testicle
viii) The
left over drug can/should be used to place a dermal incisional block
ix) The total time for this procedure should be 1 to 2 minutes
x) Drugs costs:
(1) 3 kg cat = $0.04
(2) 55 kg dog = $0.65
xi) Videos
| IT Block in 16 kg canine |
Incisional block in 16 kg canine |
 |
 |
| |
|
f) Intra-articular Injections
i) Lidocaine
(1) 2 mg/kg (1 mg/lb)
(a) With epinephrine prior to arthrotomy to help control hemorrhage
(b) Without epinephrine after joint closure
ii) Bupivacaine
(1) 1.0 mg/kg (0.5 mg/lb) after closure
iii) Generally, 4 - 6 ml fills a stifle
iv) Place in joint after closure or place lidocaine w/epinephrine in
joint before arthrotomy, wait 5 minutes, then proceed with surgery
g) Mandibular Block
i) Palpate foramen digitally from oral cavity to guide needle
ii) Use 0.5 to 1.5 ml total volume
iii) Effective coverage includes:
(1) Lower teeth
(2) Skin and mucosa of lower lip
h) Maxillary Block
i) 1.5 cm caudal to medial canthus
ii) Just ventral to zygomatic arch and ahead of the ramus
iii) Use 1.0 to 1.5 ml total volume
iv) Effective coverage includes:
(1) Maxilla and upper teeth
(2) Nose and upper lip
i) Intercostal blocks
i) Block 2 spaces ahead and behind intercostals incision
ii) Place 0.25 to 1.0 ml per site along the caudal border of each rib
near the level of the intervertebral foramen
(1) Do not exceed the dose guidelines above |